Building collapses pose significant risks to the safety of both the structures and their occupants and bystanders.
In addition to Egypt, several incidents of buildings abruptly collapsing have occurred in both Africa and the Middle East, leading to tragic outcomes.
In this guide, we will help you understand the issue and perhaps provide ideas to avoid such incidents in the future.
By adhering to stringent building codes and undertaking thorough inspections throughout the construction process, stakeholders can greatly reduce the likelihood of such disasters. Structural integrity is paramount, and understanding the factors contributing to building failures is essential for prevention.
From soil analysis to material selection, each step in construction plays a critical role in ensuring stability. Implementing preventive measures and remaining vigilant can help avoid catastrophic consequences. Understanding these principles equips builders and property owners with the tools necessary to protect against potential collapses.
In addition to proactive measures, knowing what actions to take during a building emergency can save lives. Recognizing the signs of structural distress and having a plan allows individuals to respond effectively when faced with a crisis. These insights will inform readers how to safeguard their properties and themselves against the risks of building collapse.

Understanding Building Collapse Risks
Building collapse poses significant risks that can arise from various factors, including structural weaknesses and external events. Understanding these risks is essential to implementing preventive measures effectively.
Types of Structural Failures
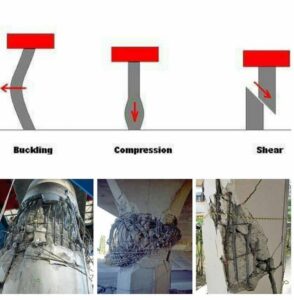 Structural failures can be categorized into several types: local failure, progressive collapse, and disproportionate collapse. Local failure occurs when a specific element, such as a beam or column, fails, compromising the surrounding structure.
Structural failures can be categorized into several types: local failure, progressive collapse, and disproportionate collapse. Local failure occurs when a specific element, such as a beam or column, fails, compromising the surrounding structure.
Progressive collapse happens when the failure of one part triggers a chain reaction, leading to a larger portion of the building collapsing. A notable example is the Ronan Point incident 1968, where a gas explosion caused a partial collapse, demonstrating how localized issues can escalate.
Disproportionate collapse refers to a situation where the structural failure is not proportional to the initial event causing it. This type can be dangerous, as even minor damage may lead to significant structural failures. Understanding these categories helps in assessing risk and employing effective remediation strategies.
Identifying Hazards in Building Structures

Identifying hazards involves assessing potential weaknesses in a building’s design and materials. Common risks include deteriorating materials, improper construction practices, and environmental factors such as soil erosion. Regular inspections should prioritize load-bearing elements, connections, and foundations.
Tools like risk assessments can help identify vulnerabilities. For instance, buildings in flood-prone areas may require enhanced foundations to mitigate risks. Technology such as structural health monitoring can provide early warnings of stress or damage, enabling timely interventions before a minor issue escalates into a collapse.
Understanding these hazards is essential for architects, engineers, and building managers to ensure safety and longevity in construction.
Design Strategies to Prevent Building Collapse
Implementing effective design strategies is crucial for ensuring the structural integrity of buildings. This section highlights the importance of adhering to building codes and employing advanced architectural and structural design approaches to mitigate the risk of collapse.
Incorporating Building Codes in Design
Building codes are essential guidelines dictating the minimum standards for construction practices. Compliance with codes like ASCE/SEI 7 ensures that structures can adequately withstand various loads, including gravity and seismic forces.
Designers should carefully evaluate the specific requirements outlined in these codes. This includes understanding load paths and ensuring that alternate ones are established, allowing forces to transfer effectively without causing failure. Reinforced concrete is often utilized to enhance a building’s resilience against these stresses, making it a preferred choice in many designs.
Furthermore, it is critical to incorporate detailed assessments of potential risks, such as blast loading or extreme weather events. This proactive approach can significantly reduce the likelihood of catastrophic failures.
Advanced Architectural and Structural Design Approaches
Adopting advanced design techniques plays a vital role in preventing building collapse. One effective method is using moment-resisting frames, which can absorb seismic loads and provide greater flexibility during an earthquake.
Incorporating shear walls into the design of high-rise buildings enhances lateral stability. These elements effectively resist lateral forces and help maintain overall structural integrity.
Employing innovative materials, such as high-strength concrete and steel, can also increase a building’s load-bearing capacity. Understanding the interactions of various forces at play during structural events is essential to effective design.
Regular assessment and retrofitting of existing structures also contribute to improved safety. These strategies ensure that older buildings meet modern design requirements, reducing their risk of collapse under unforeseen circumstances.
Frequently Asked Questions
This section addresses common inquiries about building collapse prevention, safe evacuation procedures, and post-collapse management. It highlights best practices, common causes of failures, and specific actions that can be taken to ensure safety and resilience in building structures.
What are the best practices for preventing structural failures in buildings?
Regular inspections and maintenance of a building’s infrastructure are crucial in preventing structural failures. Implementing a robust quality assurance program during construction ensures compliance with safety regulations.
Additionally, using high-quality materials and following established engineering principles can significantly enhance a structure’s durability. Continuous education and training for contractors also contribute to reducing risks.
How can one safely evacuate a building during a collapse?
Staying calm and following established evacuation routes is essential in the event of a collapse. Individuals should avoid elevators and proceed to stairwells or designated exits.
Using hands to shield the head and neck can help minimize injury during a partial collapse. Knowing the nearest exits ahead of time can greatly improve evacuation efficiency.
What are the common causes of building collapses, and how can they be remedied?
Poor design, inadequate materials, and foundation issues are common causes of building collapses. Addressing these problems through thorough engineering assessments and high-quality construction practices can mitigate risks.
Implementing regular structural evaluations and promptly addressing maintenance concerns also play a vital role in preserving the building’s integrity.
How do earthquake-resistant construction techniques prevent building collapse?
Earthquake-resistant construction techniques use flexible materials and innovative design strategies. These methods allow structures to absorb and dissipate seismic energy, reducing the risk of collapse.
Reinforced foundations and strategic bracing enhance stability during seismic events, ensuring the building can withstand tremors effectively.
During a building collapse, what are the safest locations within the structure?
The safest locations during a building collapse typically include interior rooms away from windows and heavy furniture. Staying under sturdy furniture can protect individuals from falling debris.
Avoiding corners or areas directly beneath heavy fixtures helps lessen risks. Awareness of surroundings and having an evacuation plan enhances personal safety.
Regarding disaster management, what steps should be taken following a building collapse?
Assessing casualties and ensuring immediate medical attention after a building collapse is crucial. Establishing communication with emergency services allows for a coordinated response.
Conducting a thorough property assessment determines further risks and necessary recovery actions. Collaborating with local authorities and rescue teams facilitates efficient disaster management efforts.





